PhD Research:
Cooking something big! Stay tuned.
Master’s Research:
Influence of Masonry Infills on Blast Response of Earthquake-Resistant RC Buildings
Team
- Shiva Baddipalli, Project Associate, IIT Mandi
- Mahipal Khulariya, PhD Research Scholar, IIT Mandi
- Dr Sandip Kumar Saha, Assistant Professor, IIT Mandi
Description
This study aims to investigate the influence of the masonry infill strength on the blast performance of the masonry infilled RC buildings designed to withstand different levels of seismic demand. Based on the extensive literature review, the specific objectives of this study are: (i) to examine the effect of the infill’s nonlinearity on the blast response of the earthquake-resistant RC buildings, and (ii) to probabilistically assess the effect of infill panel strength and seismic design level on the blast response of the considered buildings subjected to the surface burst. It is observed that the consideration of infill’s nonlinearity influences the blast response up to a certain scaled distance only. Moreover, increasing the infill strength does not necessarily enhance the blast performance; however, designing the building to higher seismic demand results in improved blast performance. In addition, proper insight into seismic design level and infill strength of any RC building is required prior to plan and design them with suitable blast-mitigation measures.
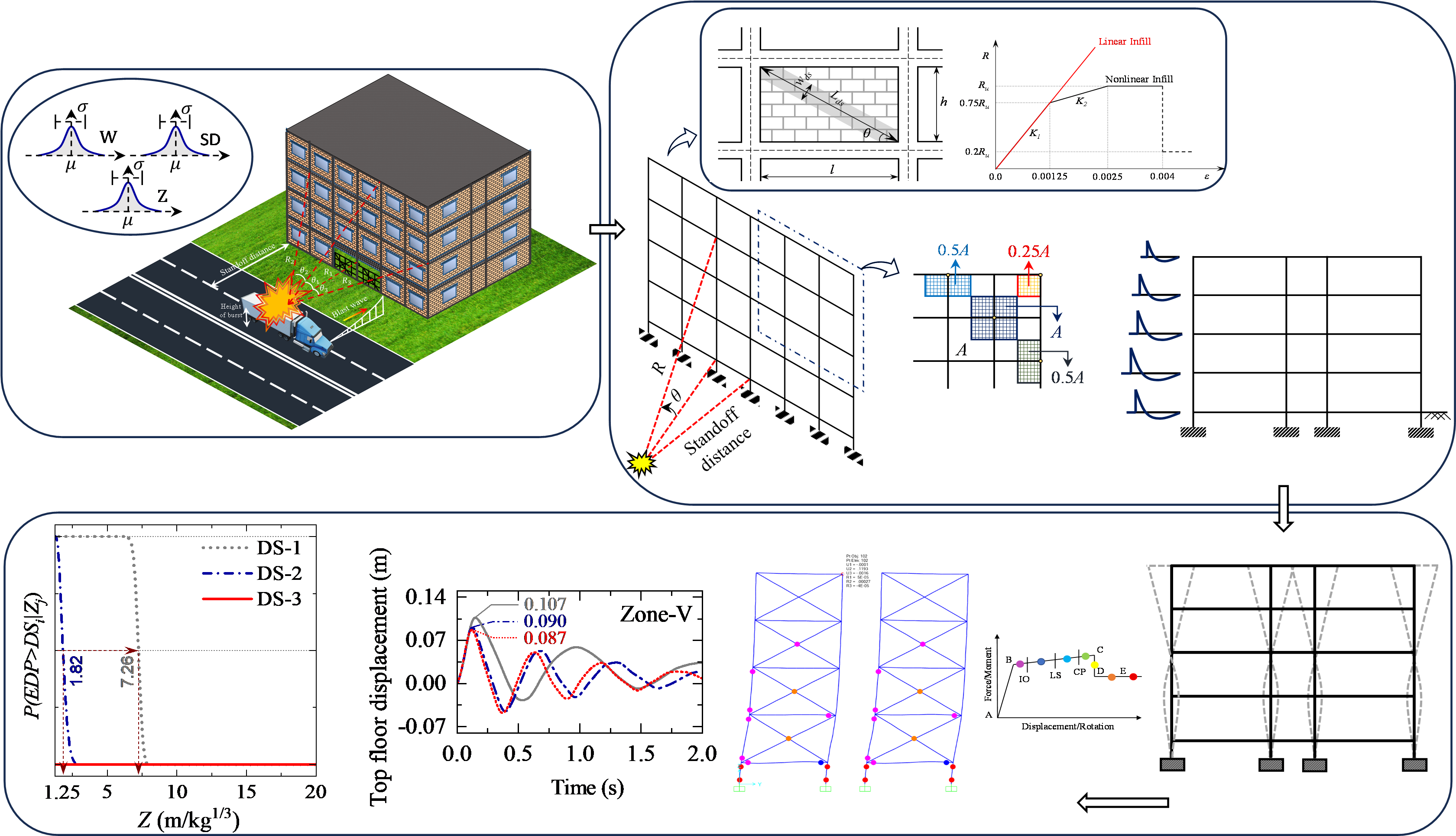
Relevant Publications
- Baddipalli, S., Kulariya, M., & Saha, S. K. (2023). Influence of Masonry Infills on Blast Response of Earthquake-Resistant Reinforced Concrete Buildings Structures. Structures, 50, 908-924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2023.02.078
Construction Practices and Seismic Vulnerability of Buildings in Indian Himalayan Region: A Case Study
Team
- Yati Aggarwal, PhD Research Scholar, IIT Mandi
- Shiva Baddipalli, Project Associate, IIT Mandi
- Dr Sandip Kumar Saha, Assistant Professor, IIT Mandi
Description
Due to rapid growth in tourism and other economic activities, several small cities and towns in the Indian Himalayan region are facing problem of unplanned construction and extended use of deteriorating old structures. Despite being in the most active zone of seismic activity, significant non-engineered construction is practiced in this region. Hence, it becomes essential to examine the existing engineered and non-engineered building typologies and assess their vulnerabilities against earthquake shaking. This study presents typical engineered and non-engineered construction practices observed through a survey of 1009 buildings located within Mandi, a small town in the lap of the great Himalayas in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. An attempt is made to identify the typical building typologies, visible structural irregular features and their seismic vulnerability. A few building typologies are found typically predominantly prevail in northern zone of Indian Himalayan region. Rapid visual screening (RVS) of the surveyed buildings is performed using different existing guidelines. It is observed that a substantial number of buildings with hybrid typology (stone masonry mixed with brick masonry or reinforced concrete) are prevailing in the study area. It is also observed that the seismic vulnerability, as per the adopted RVS guidelines, of majority of the buildings is high, indicating urgent demand for safeguarding the vulnerable built environment and develop the framework for seismic resilient society. It is further concluded that use of region-specific vulnerability attributes can improve the segregate of buildings based on the expected damage.
Relevant Publications
- Aggarwal, Y., Baddipalli, S., & Saha, S. K. (2023). Construction Practices and Seismic Vulnerability of Buildings in Indian Himalayan Region: A Case Study. Natural Hazards Review, 25(2), p.05024002.https://doi.org/10.1061/NHREFO.NHENG-1902
